We constantly receive messages alerting us that our standard of living is unsustainable. However, we rarely receive accurate information on what we can do, beyond changing the light bulbs in our house.
We may feel overwhelmed when we see that our way of life is unsustainable. We are facing a very serious and unprecedented environmental crisis, in the face of which people are powerless and help
09 – ARTIFICIAL PRESERVATIVES
It’s “common” for food to contain artificial preservatives. That’s because they can “prevent spoilage, improve appearance and texture, and maintain the food’s nutritional quality”. It’s not just fast food restaurants using artificial preservatives, either.
There are also natural preservatives — like salt, sugar, vinegar and citrus juice — but using them usually comes at a
10 – SELECTIVE WASTE COLLECTION AND RECYCLING
Learn about the benefits of selective waste collection and recycling on the environment and society.
Selective collection and recycling often reduce the negative impact of waste affecting the environment and society.Selective waste collection involves the management of waste, by their temporary storage, by categories, in specially arranged places, for recycling.Recycling is the collection, sep
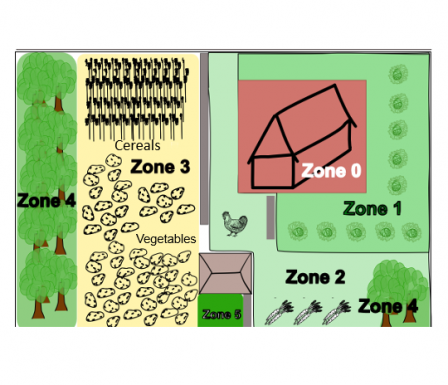
07 – PERMACULTURE ZONING
Permaculture zones help us organize our spaces according to how (and how often) we use them. As a design strategy, zones are a super powerful way to make choices about where to place elements of the ecosystem, in order to enhance their ecological performance. Try to imagine: how could these zones be envisioned? In our micro training, you will get more practical experience about how this principle
06 – WATER USAGE
Learn the sources of water and how it is used by humans.
70% of our Earth’s surface is water93.8% is ocean water, 2.5% is fresh water0.375% is accessible to humans0.3% of water is in lakes & ponds0.06% is in soil & forests, 0.03% is in rivers,0.035% is in the atmosphere.
Sources of water in the environment:
13% of precipitation is rain86% of precipitation is from condensation
05 – GARDEN EXPLORATION
Our aim is to discover the biodiversity in our own neighbourhoods and also the threats to it. Due to the direct experience and contact with the diversity and endangered species we get a more tangible awareness about biodiversity and our impact on it.
Download the app “PlantNet” and scan the first plant you find in your house or neighborhood, and get familiar with the different options of t
04 – HOW MUCH SUNLIGHT DOES EACH PLANT NEED?
Learn about the needs of plants to make the best use of your garden space.
At first sight, a permaculture garden may seem a bit messy, but in reality there is a lot of planning involved. For example, when it comes to distributing the plants in the garden, we can make better use of the space if we know the sunlight needs of each plant and thus reserve the shaded areas for the less demanding one
02 – THE ECO-SYSTEM AROUND US
We want to deepen the understanding about how the diverse elements of a living eco-system are interconnected.
An ecosystem includes all the living things in a give area interacting with each other and also with their non-living environement. In a eco-system we can find four (4) components:1) Abiotic substances: Mineral elements. Organic compounds. Water Physical matters, e.g., sunlight, wind,
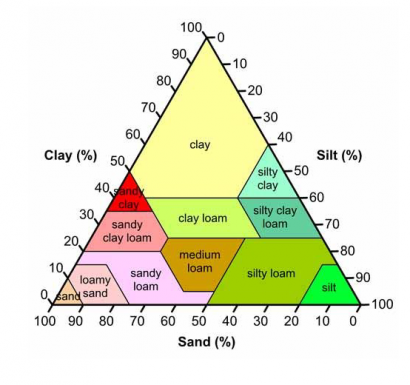
03 – SOIL TEXTURE
Have you ever realized how important the soil is?
Soil is the foundation of every kind of ecosystem living on earth. When planting and growing food, soil becomes a fundamental aspect to take into consideration. Soil testing is a key tool in sustainable soil management and allows us to monitor in time what’s the impact of our activities in terms of soil regeneration.
Do you want to learn m
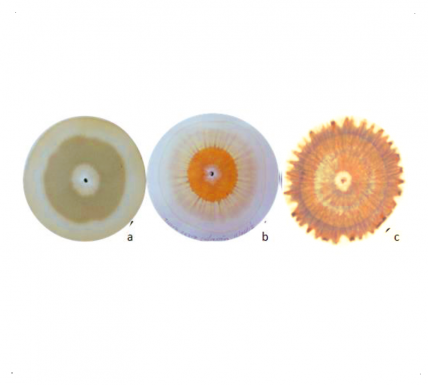
01 – SOIL HEALTH
Soil is the great neglected element of conventional agronomy. Look at the difference in richness between conventional and organic soil.
The soil of our vegetable garden is the central element. We can know its composition with analyses like this one (Pfaiffer chromatography) where it is separated into its different components. Here we see a soil of traditional agronomy (a) that only retains